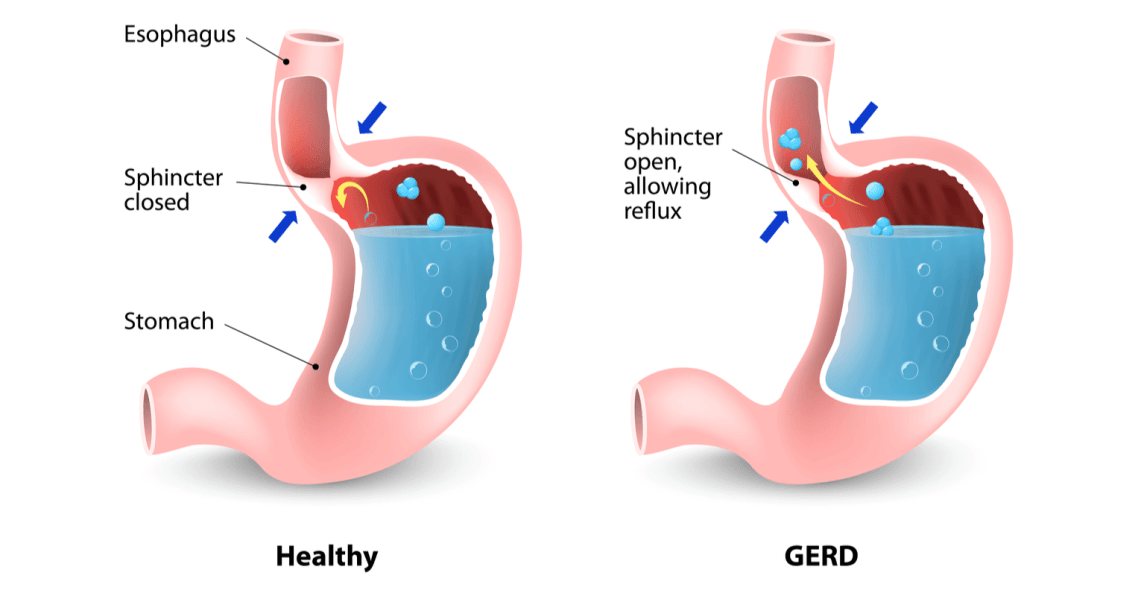
According to Dr. Arush Sabharwal:
Obesity-related changes in the Stomach and Esophagus (food pipe) contribute to an explanation for this association. Obese people are at higher risk for Hiatus Hernia, Lax lower esophageal Sphincter (muscle) and other diseases. Similarly, in a US study, the analysis of esophageal pH in patients with GERD demonstrated that obese individuals had a fivefold increase in risk of abnormal total acid exposure (which provides a more objective assessment of reflux) compared with those of normal weight. Additionally, they found that a mechanically defective lower esophageal sphincter was over-represented in patients who were obese compared with those of normal weight. The association between obesity and GERD might also be mediated by increased estrogen exposure in individuals who are obese.